15 Unexpected Ways Animals Have Influenced Human Innovations
Animals have long been a source of inspiration for humankind, though their influence often goes unnoticed. Yet, when we look closely, birds, insects, and mammals reveal secrets that spark groundbreaking ideas.
From the delicate patterns on a beetle’s wings to the sophisticated communication systems of dolphins, our fellow creatures offer countless lessons worth exploring. Each new discovery reminds us that nature and technology share an extraordinary bond.
Below are 15 intriguing examples of how these living wonders have helped shape our creations.
Ingenious Bee Patterns
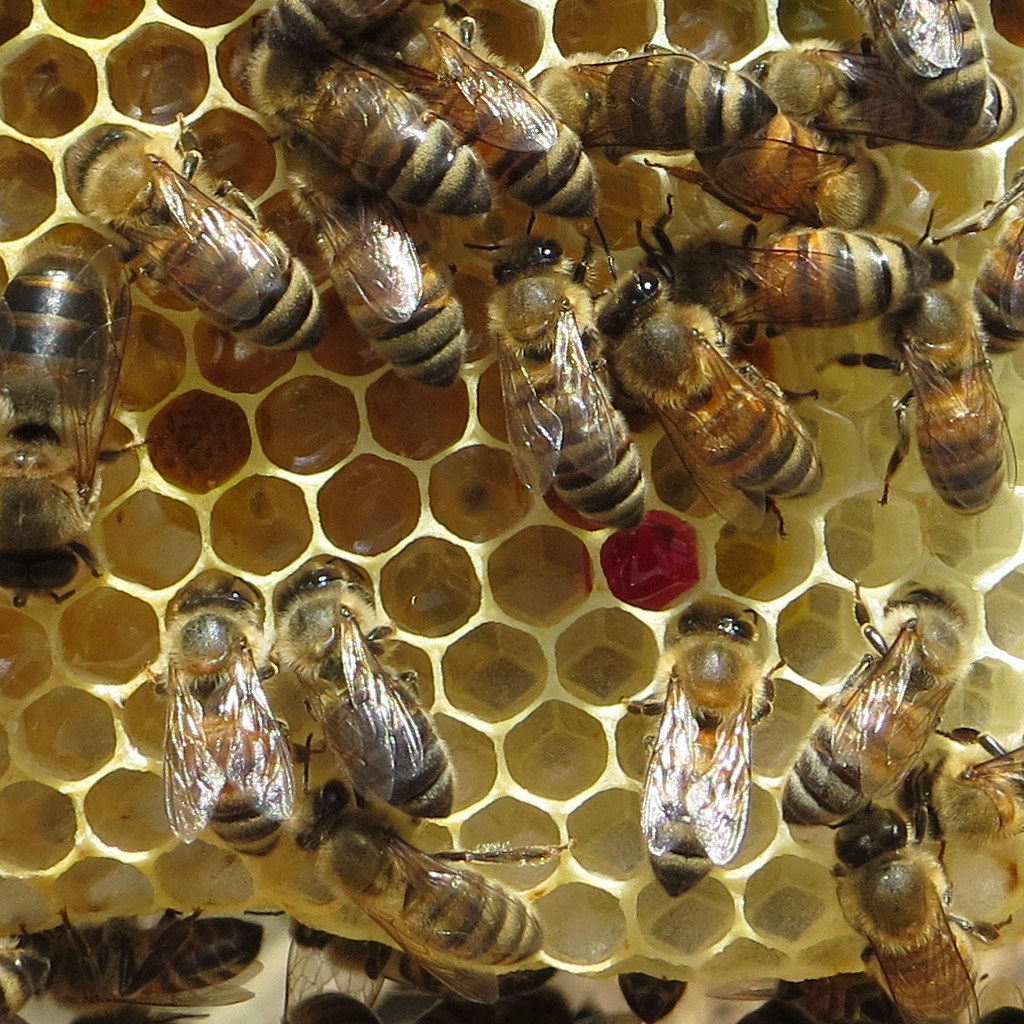

The hexagonal structures found in honeycomb have guided architects and engineers for centuries. Ancient Greek buildings, for instance, borrowed hexagonal pillars in some designs to balance stability with efficient use of materials.
Bees construct their hives to maximize space while minimizing waste, which directly influenced modern packaging and aerospace designs. Today, researchers continue to analyze bee colonies to develop more sustainable building materials that require fewer resources.
Sticky Insights from Geckos
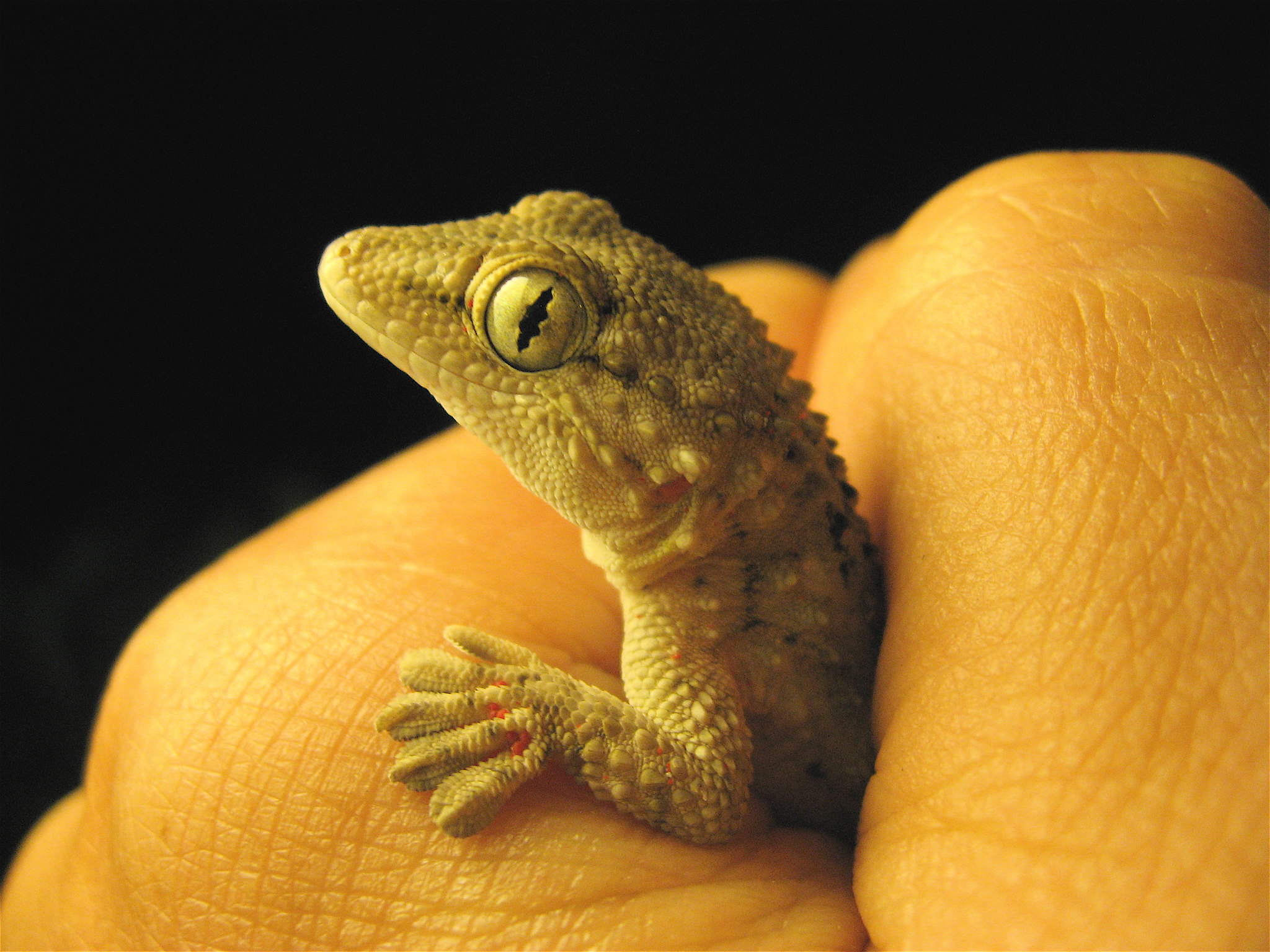

The remarkable grip of geckos’ feet has led to the development of adhesives that leave almost no residue. Scientists in research labs around the world study the microscopic hairs on gecko toes to replicate their clinging power.
These gecko-inspired materials now appear in robotics, allowing machines to climb walls without damaging surfaces. They also hold promise in medical settings, where gentle yet secure bandages could prevent skin irritation.
Like Go2Tutors’s content? Follow us on MSN.
Termite-Inspired Cooling Techniques
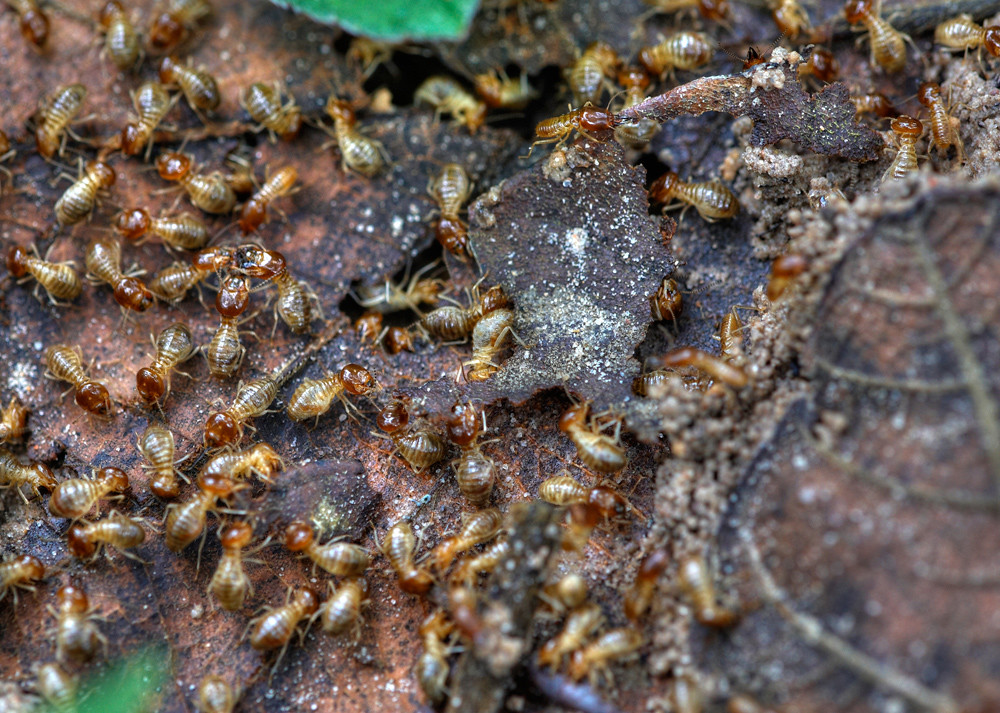

The mounds built by termites in parts of Africa have motivated architects to reduce energy usage. Termite structures maintain consistent temperatures inside by channeling airflow through cleverly placed vents.
Observers noted these natural air-conditioning systems and adapted them into sustainable building designs in hot climates, including several office complexes in Harare, Zimbabwe. By applying termite-inspired ventilation, these modern buildings stay cool without relying heavily on electricity.
Shark Skin Enhances Hydrodynamics
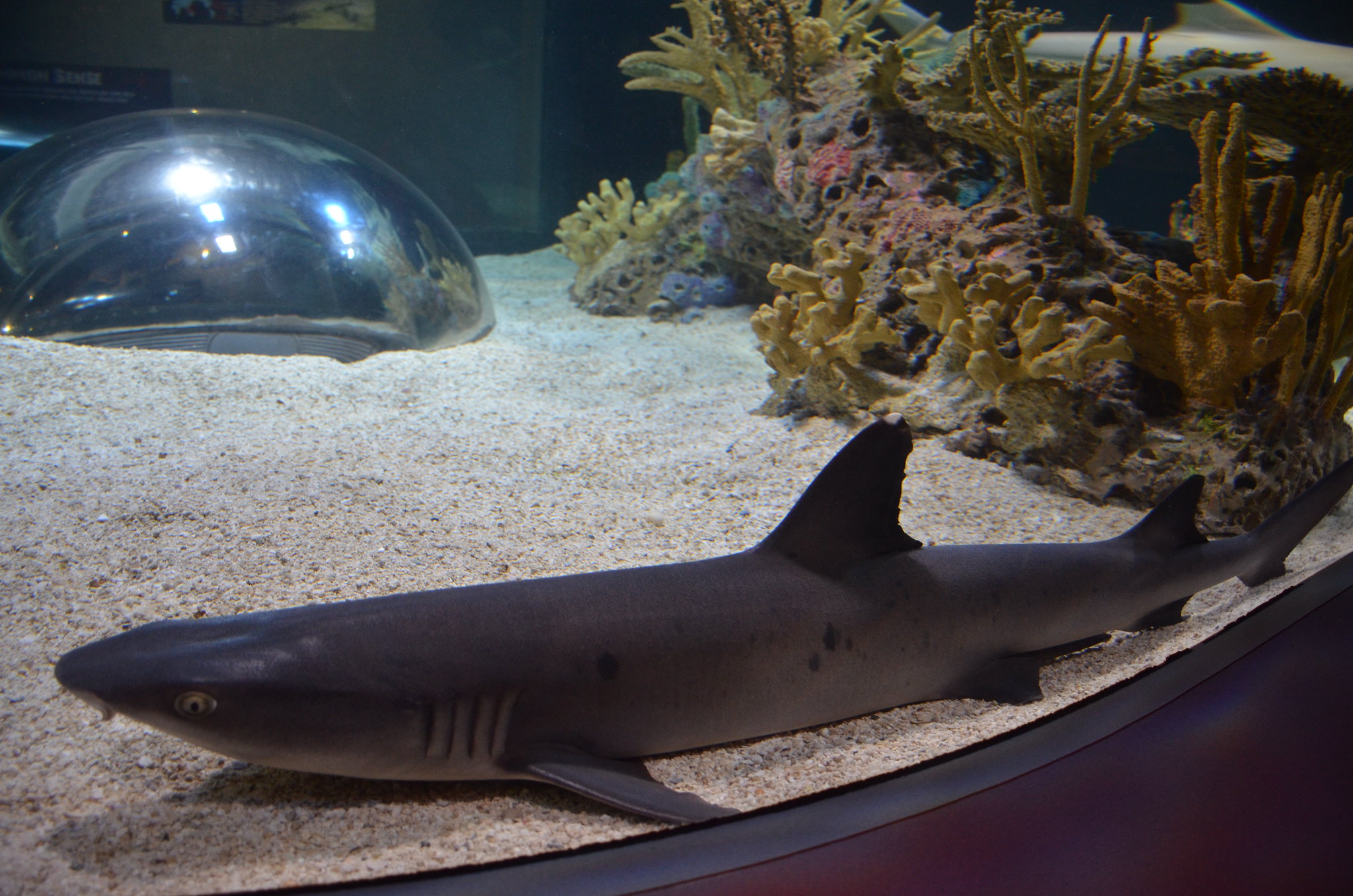

Sharks glide through the water with minimal resistance, thanks in part to tiny tooth-like scales on their skin. Engineers studied this texture to develop surfaces for boats, submarines, and competitive swimwear that cut through water more efficiently.
Some Olympic swimmers have even worn suits mimicking shark skin to gain a competitive edge. Beyond sports, scientists continue exploring similar textures to reduce fuel consumption in large ships.
Kingfisher-Designed Trains
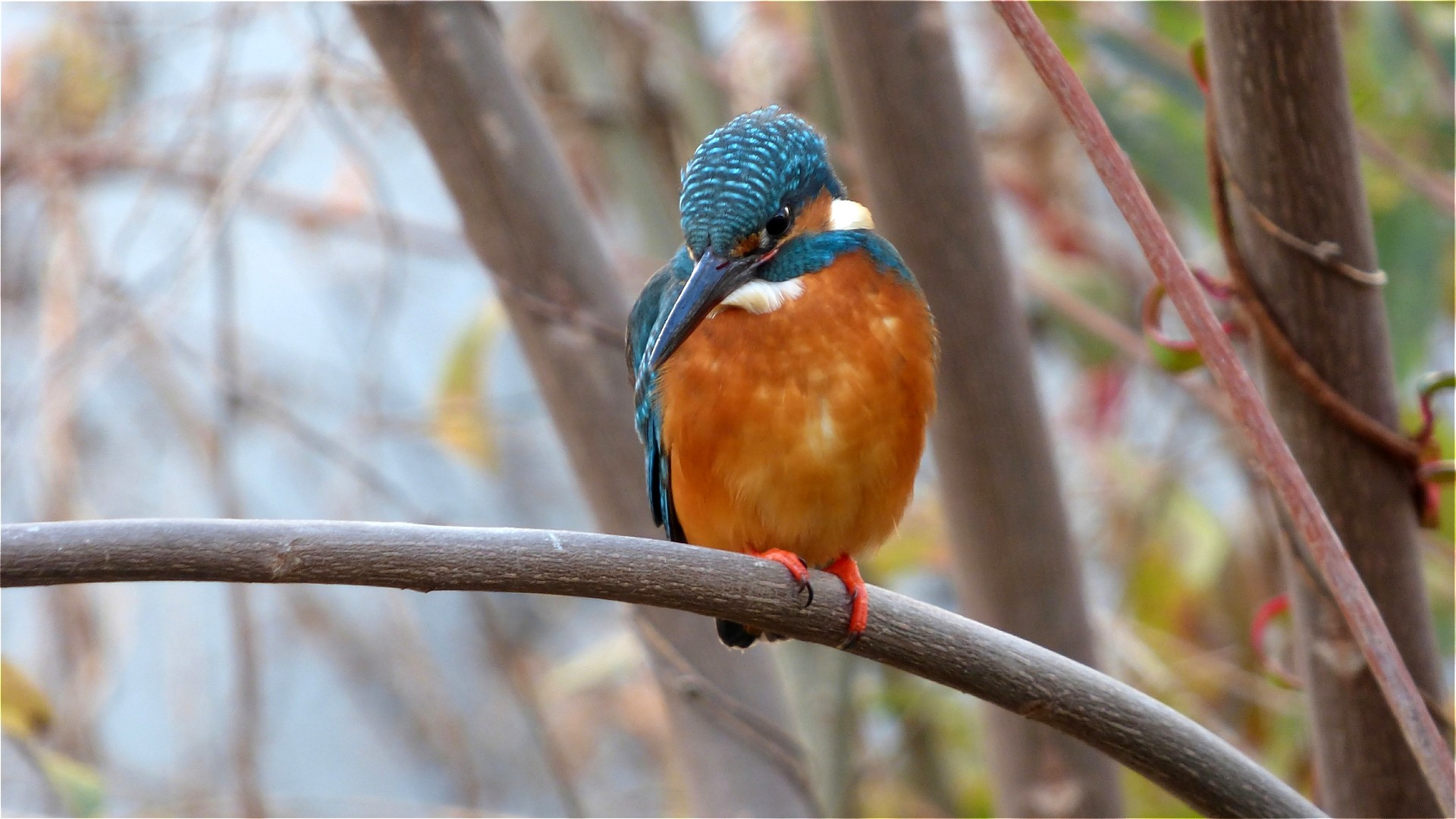

The rapid dive of a kingfisher hunting fish sparked ideas for high-speed train noses. Early Japanese bullet trains created a loud boom exiting tunnels, so engineers turned to the kingfisher’s streamlined beak for a solution.
By reshaping the front car to resemble this bird’s profile, they reduced noise and improved energy efficiency. Commuters in Japan now travel more quietly and swiftly, proving nature’s guidance can transform mass transit.
Like Go2Tutors’s content? Follow us on MSN.
Woodpecker-Inspired Helmets
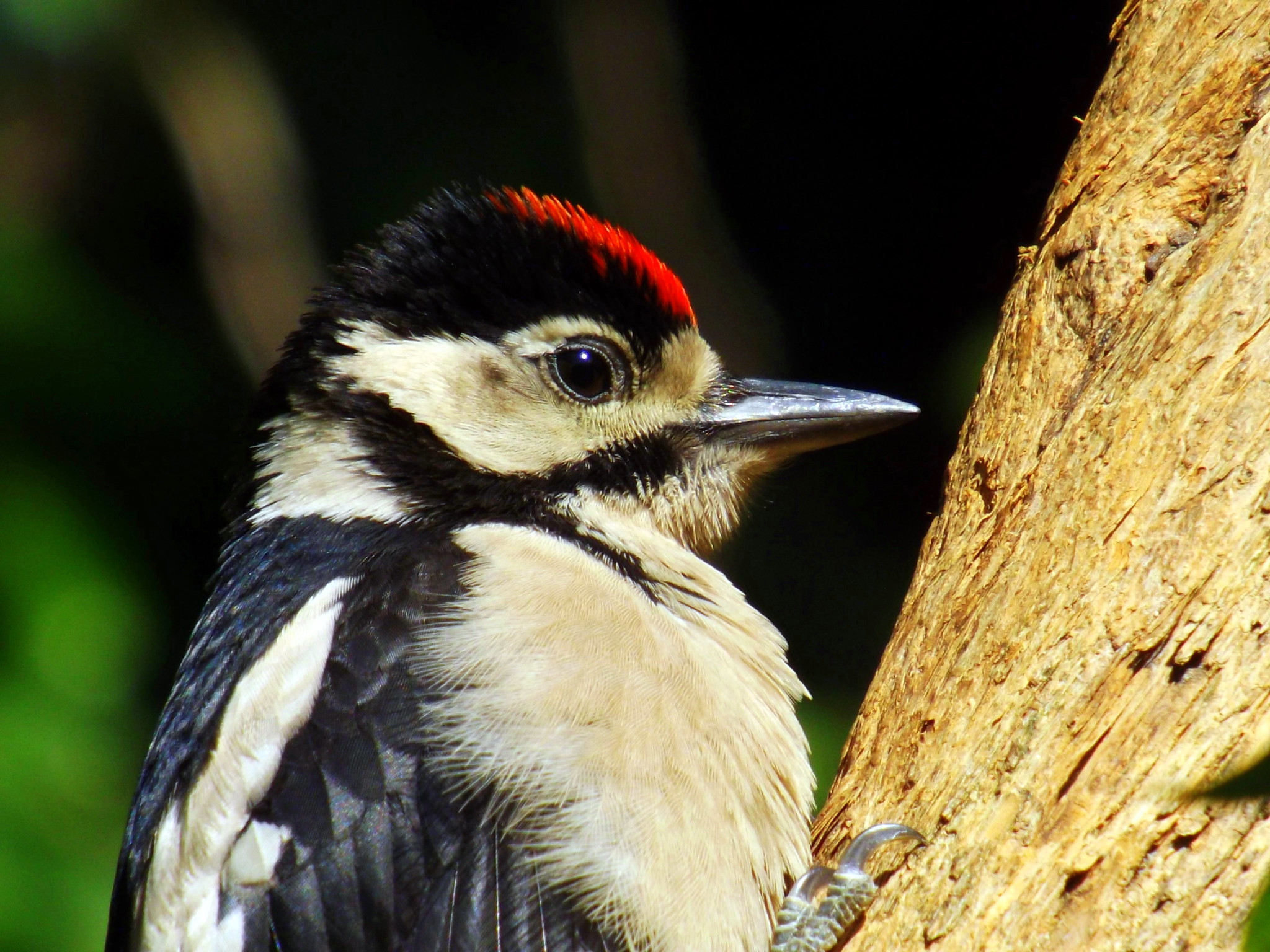

Woodpeckers strike tree trunks at high speeds yet remain unharmed, and researchers wondered how. Upon examining their skulls, they discovered specialized bone structures that absorb shock.
Companies designing sports helmets and protective gear borrowed these biological adaptations to create safer equipment for athletes and cyclists. The woodpecker’s unique anatomy continues to inform innovations aimed at reducing head injuries.
Moth Eyes and Anti-Reflective Surfaces
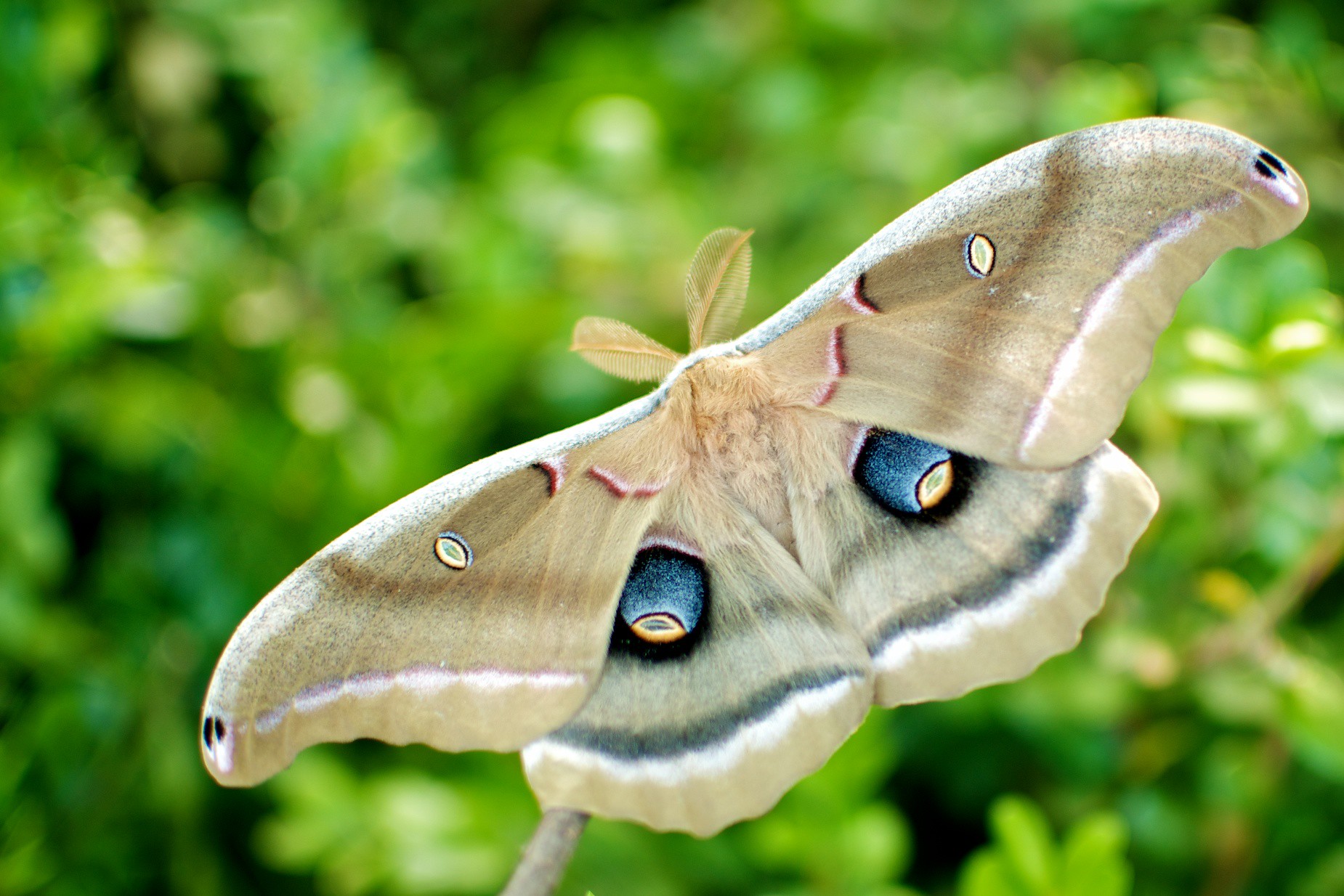

Moths navigate nighttime environments using eyes that minimize reflection and glare. Their eye structures inspired scientists to create anti-reflective coatings now used on camera lenses, solar panels, and smartphone screens.
By observing how moths reduce light reflection to avoid predators, developers have made gadgets more efficient and images clearer. Even astronomy equipment has benefited, enhancing the quality of telescope lenses for stargazers.
Clingfish Suction Lessons
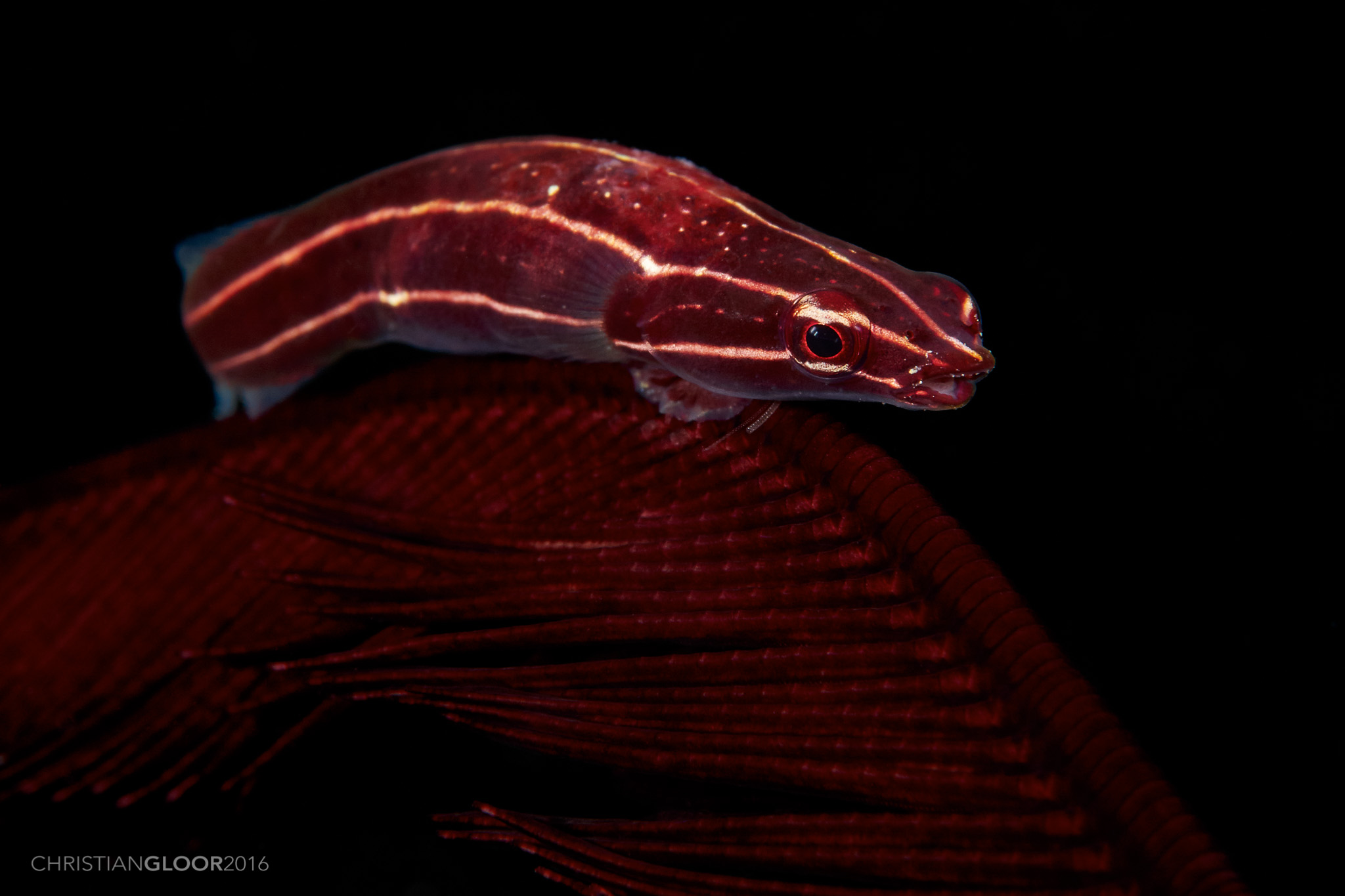

Clingfish possess a suction disc on their bellies that firmly attaches to wet, slimy surfaces. Observers have replicated this feature in medical devices that need strong but easily removable grips.
Hospitals have started testing clingfish-inspired suction cups for handling sensitive tissue during surgery. This discovery offers a glimpse of how a small marine creature can influence major advancements in healthcare.
Like Go2Tutors’s content? Follow us on MSN.
Bats and Advanced Echolocation Devices
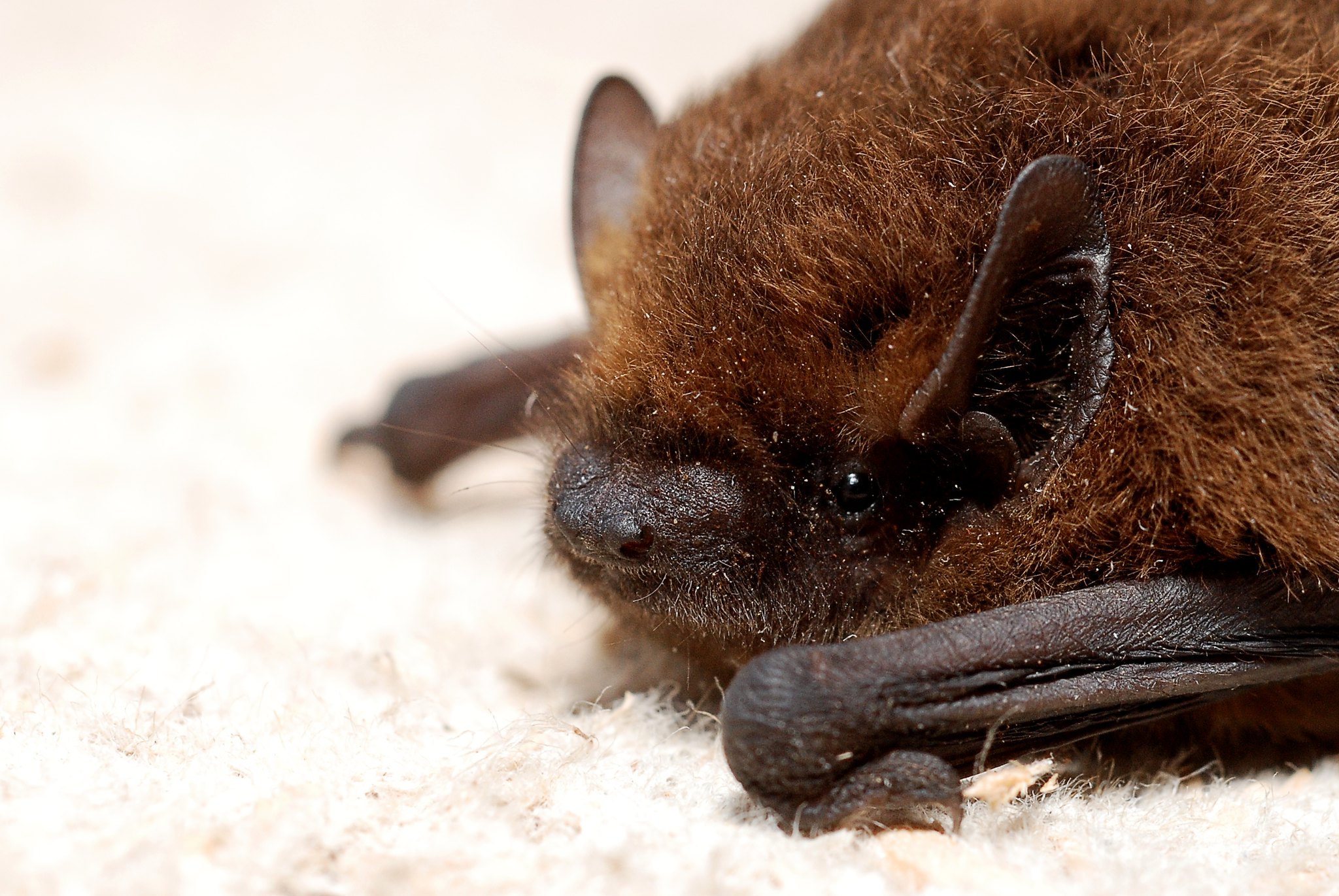

Bats rely on echolocation to find food and navigate dark caves with remarkable precision. That same principle underpins sonar systems, which help ships detect obstacles underwater.
Researchers further adapted echolocation concepts to design walking aids for the visually impaired, allowing them to sense obstacles through sound waves. The bat’s natural sonar has paved the way for assistive technology that can drastically improve everyday safety.
Butterfly Wings and Nanotechnology

Butterfly wings boast tiny scales that scatter light, creating vibrant colors without pigments. This phenomenon sparked new approaches in nanotechnology, where engineers manipulate surfaces at the microscopic level to produce more vivid displays.
Cosmetic companies also use butterfly-wing research to develop long-lasting colorants that stay bright. By studying how these insects dazzle the eye, innovators have discovered methods for efficient, eco-friendly color production.
Dolphin Communication in Sonar
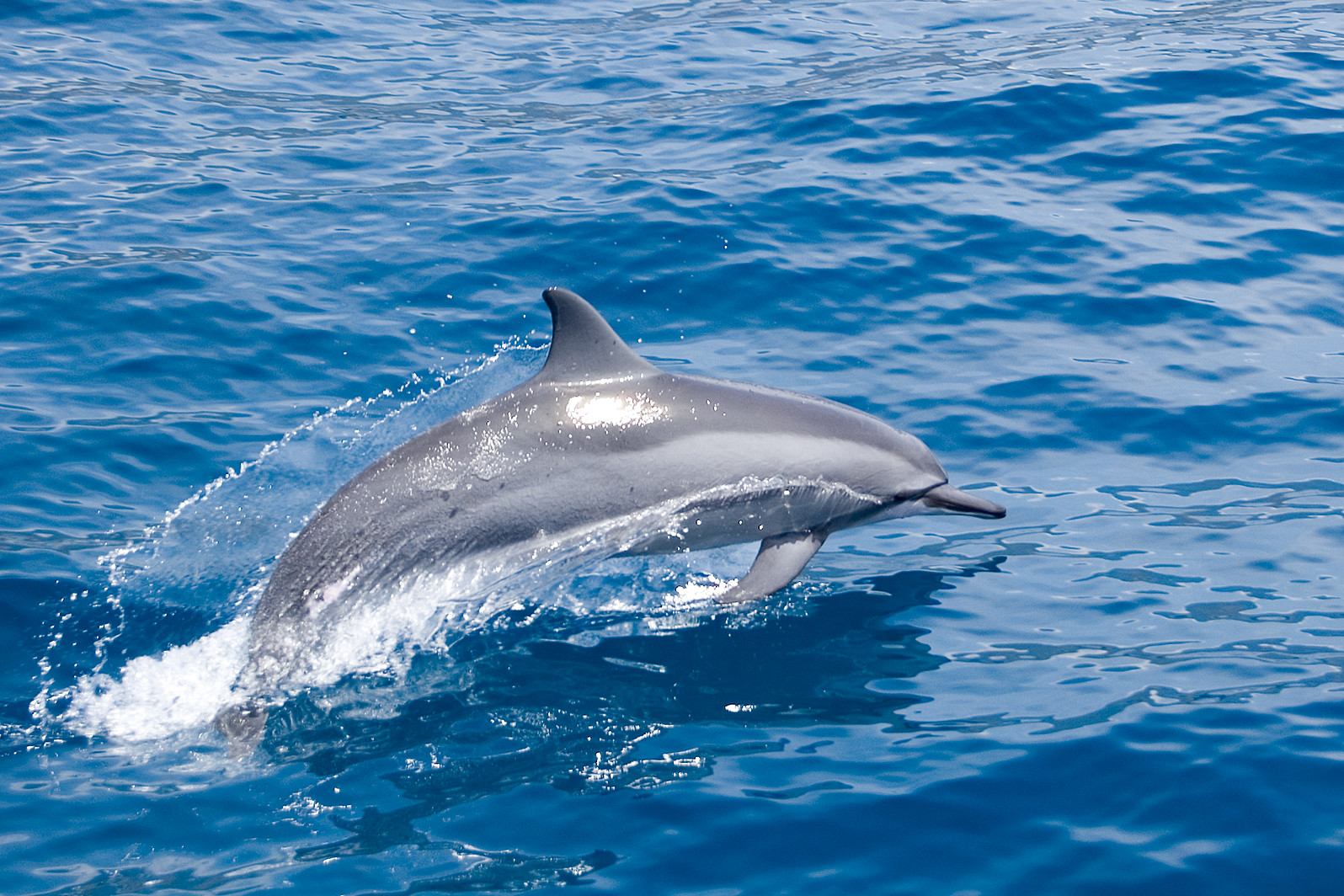

Dolphins utilize clicks and whistles to communicate with one another across vast ocean distances. Their ability to distinguish multiple signals simultaneously shaped modern sonar and underwater communication techniques used by submarines.
Some technology firms are examining these marine mammals’ methods to improve speech recognition software. The dolphin’s vocal repertoire showcases the potential of natural acoustics to transform how we share information.
Like Go2Tutors’s content? Follow us on MSN.
Spider Silk and Ultra-Strong Fibers
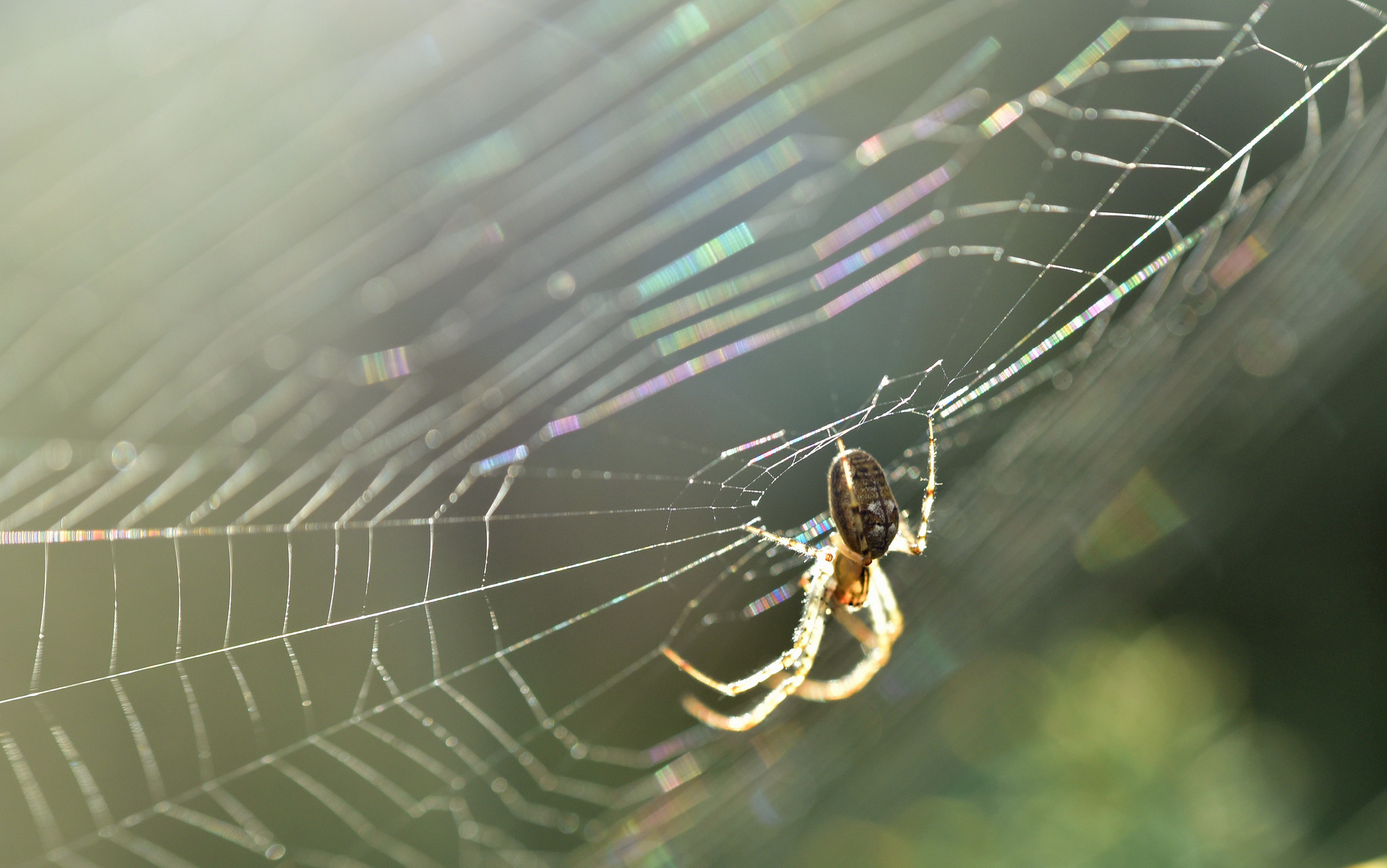

Spider silk is revered for its toughness, elasticity, and light weight. Modern textile manufacturers study this silk to create flexible yet durable materials for military gear and medical sutures.
Research labs continue to experiment with producing synthetic spider silk that can withstand extreme stress while remaining comfortable to wear. The spider’s humble web has become a model for anyone seeking resilient, sustainable fabrics.
Fireflies and Efficient LED Lighting
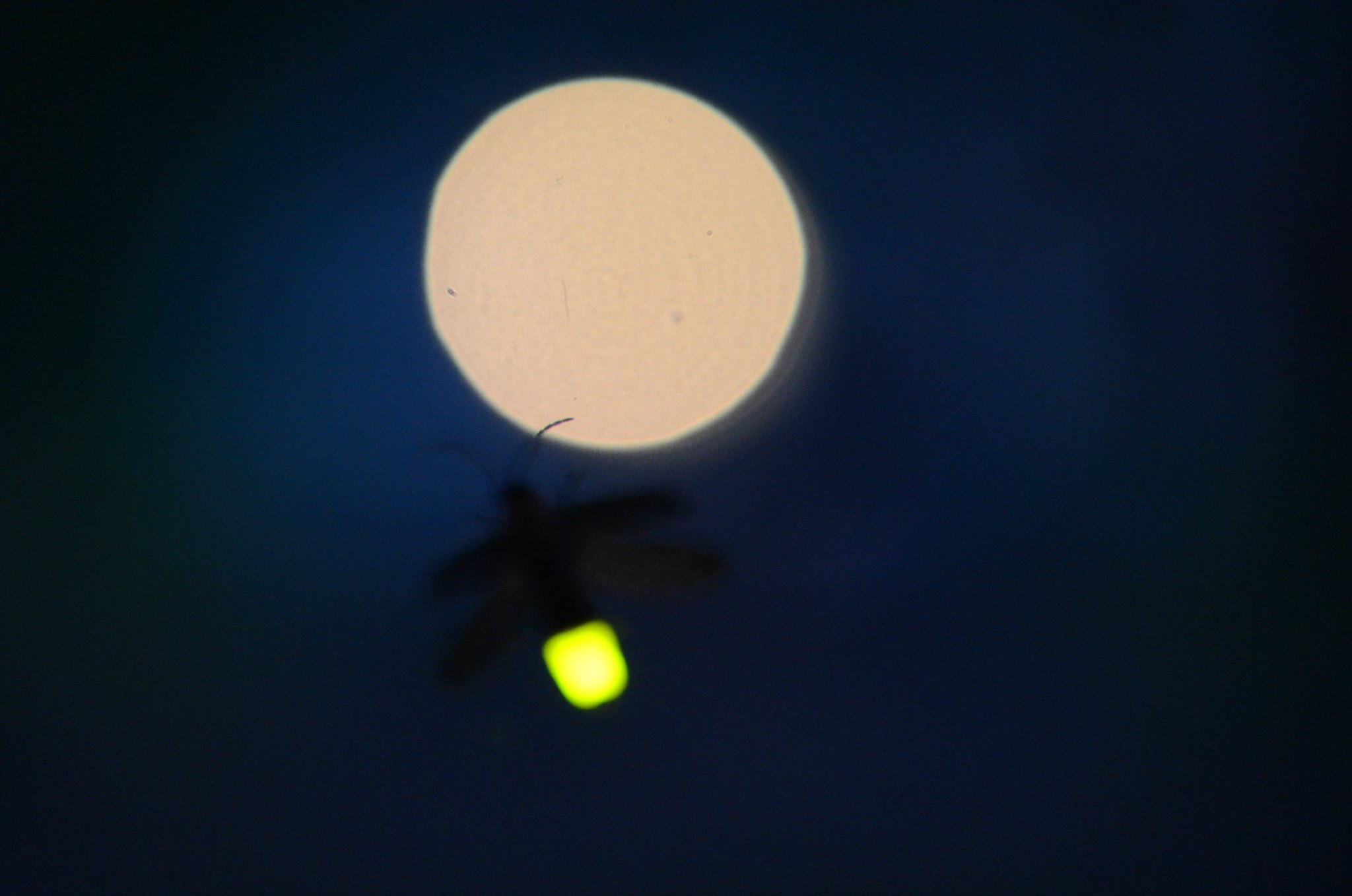

The bioluminescent glow of fireflies illuminates summer nights and has also guided lightbulb innovation. Scientists discovered that the unique microstructure of a firefly’s exoskeleton enhances light emission.
Engineers applied those insights to craft more efficient LED bulbs, reducing energy consumption and improving brightness. The firefly’s gentle sparkle now shines on city streets and in living rooms worldwide.
Cat Whisker Sensors

Cats rely on sensitive whiskers to navigate tight spaces and detect subtle changes in their environment. Taking a cue from these felines, researchers developed sensors that measure airflow and pressure with extreme accuracy.
These “whisker-like” devices have found their way into robotics, helping machines gauge distance and avoid collisions. Cat whiskers prove that even the smallest biological feature can inspire groundbreaking technology.
Like Go2Tutors’s content? Follow us on MSN.
Beaver Dams and Water Management

Beavers shape entire ecosystems by constructing dams that slow water flow and create wetlands. This natural engineering has influenced conservationists to design similar structures that reduce erosion and restore habitats.
In some regions, officials have reintroduced beavers to help manage local waterways more sustainably. Observing how beavers manipulate their surroundings reminds us that working with nature often yields the most effective solutions.
A Continuing Journey of Discovery

Every new invention sparked by animal life underscores the depth of knowledge hidden in the natural world. From sticky gecko toes to resilient spider silk, creatures large and small continue to steer scientific breakthroughs.
Looking around, it’s easy to wonder what other animal secrets might still be uncovered. Paying attention to these remarkable adaptations encourages us to develop technologies that coexist harmoniously with our environment.
More from Go2Tutors!

- Famous Battles: How Much Do You Really Know About U.S. History?
- Top 5 Most Important Skills, According To Harvard Business School
- How Well Do You Know 90s Pop Culture? Take the Quiz
- Master the Art of Public Speaking with These Expert Tips
- Think You Know Capitals? Put Your Knowledge to the Test
Like Go2Tutors’s content? Follow us on MSN.