15 Little-Known Facts About the Human Body
The human body is an extraordinary marvel of biological engineering, harboring countless mysteries and surprising capabilities that most people never learn about.
While we live in these remarkable vessels every day, there are numerous fascinating facts about our bodies that remain largely unknown to the general public. Let’s explore some of the most intriguing and lesser-known aspects of human physiology.
Bone Regeneration
Your skeleton completely replaces itself every decade through a continuous process of bone remodeling. This remarkable regeneration occurs through specialized cells called osteoclasts breaking down old bone tissue while osteoblasts build new bone.
Your body maintains this delicate balance throughout your entire life, though the process slows with age.
Crystalline Eyes

The protein crystals in your eyes are the only naturally occurring crystalline structures in the human body. These specialized proteins in your eye lenses are arranged in a precise crystalline pattern that allows light to pass through clearly.
These biological crystals are essential for maintaining the transparency of your eye lenses.
Like Go2Tutors’s content? Follow us on MSN.
Stomach Acid Power

Your stomach acid is strong enough to dissolve metal, yet your stomach doesn’t digest itself thanks to a specialized mucus layer. This powerful acid, with a pH between 1.5 and 3.5, could easily create holes in a cotton tablecloth.
Your stomach produces a new protective mucus layer every two weeks to prevent self-digestion.
Taste Bud Turnover

Your taste buds completely regenerate every two weeks, making them one of the most frequently renewing tissues in your body. This rapid turnover ensures that your sense of taste remains sharp and accurate.
Each taste bud contains between 50 and 100 taste receptor cells that are constantly being replaced.
Brain Electricity

Your brain generates enough electricity while you’re awake to power a small LED light bulb. This electrical activity comes from the billions of neurons communicating through electrical impulses.
Your brain continues this electrical activity even during sleep, though at different frequencies and patterns.
Like Go2Tutors’s content? Follow us on MSN.
Microorganism Universe

There are more microorganisms living in and on your body than there are stars in the Milky Way galaxy. These trillions of microscopic organisms, collectively known as your microbiome, play crucial roles in your health.
Many of these organisms are actually essential for your survival and well-being.
Fingernail Growth Patterns

Your fingernails grow at different rates depending on which finger they’re on, with the middle finger growing the fastest. The growth rate also varies between your dominant and non-dominant hand.
Fingernails generally grow about 3.5 millimeters per month, with the middle finger outpacing others by a small margin.
Internal Length
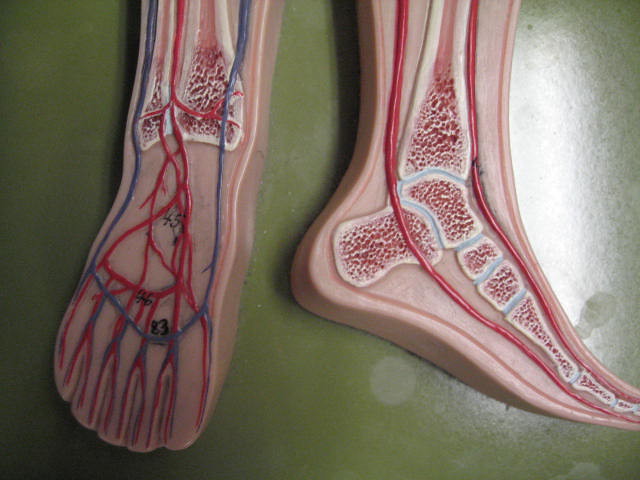
If you were to stretch out all the blood vessels in your body end to end, they would extend about 60,000 miles. This vast network of arteries, veins, and capillaries could circle the Earth more than twice.
The majority of this length comes from the countless tiny capillaries that deliver oxygen to every cell.
Like Go2Tutors’s content? Follow us on MSN.
Nocturnal Height Changes

You’re actually slightly taller in the morning than you are at night, typically by about half an inch. This height difference occurs because the cartilage discs between your vertebrae compress throughout the day under the force of gravity.
These discs decompress while you sleep in a horizontal position.
Unique Tongue Print
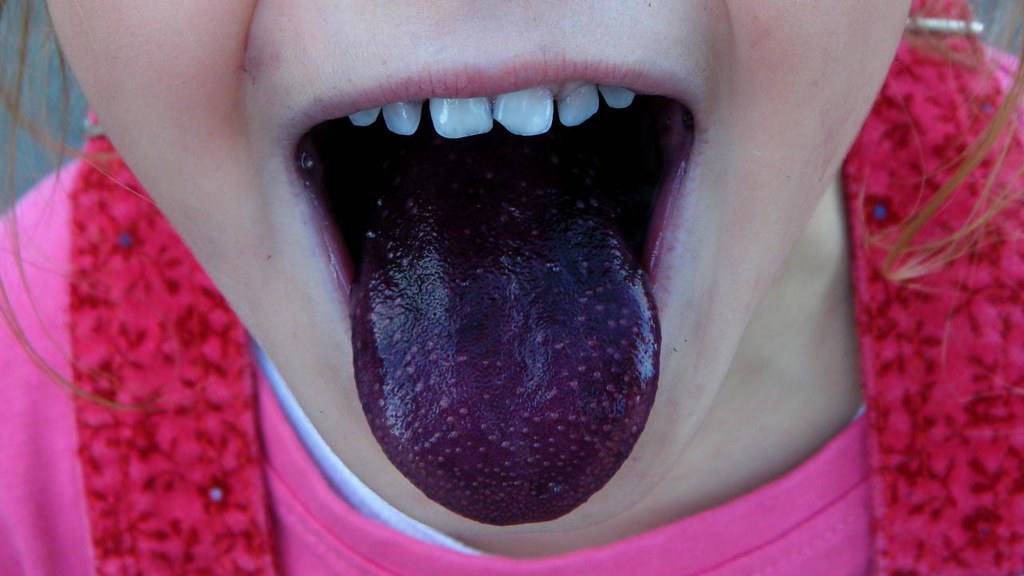
Like fingerprints, every person’s tongue print is unique and could theoretically be used for identification. The pattern of bumps, ridges, and texture on your tongue is entirely individual to you.
Some biometric researchers have suggested tongue printing could become a future security measure.
Hair Strength

A single strand of healthy human hair can support up to 100 grams in weight before breaking. Scaled up, a full head of hair could theoretically support the weight of two elephants.
The secret lies in the complex structure of keratin proteins that make up each hair strand.
Like Go2Tutors’s content? Follow us on MSN.
Continuous Eye Movement
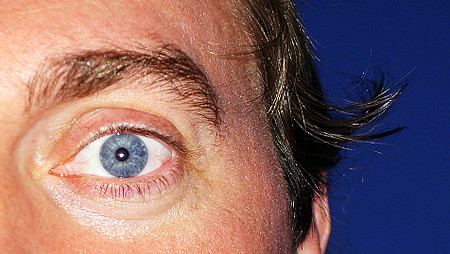
Your eyes make approximately 100,000 movements each day and can distinguish about 10 million different colors. These constant movements, called saccades, help your brain build a complete picture of your surroundings.
Even when you think you’re staring straight ahead, your eyes are making tiny movements.
Living Bones
Your bones are constantly alive and active, containing various types of living cells, blood vessels, and tissues. Far from being inert supports, bones are dynamic organs that store minerals, produce blood cells, and continuously rebuild themselves.
They even have their own sensory nerves and pain receptors.
Healing Speed
The cells in your body exhibit different healing rates, with mouth wounds healing faster than those anywhere else on your body. This accelerated healing occurs because saliva contains special compounds that accelerate wound healing.
Additionally, the mouth has more blood vessels to supply healing factors.
Like Go2Tutors’s content? Follow us on MSN.
Brain Processing Power
Your brain processes images you see in as little as 13 milliseconds, faster than you can consciously register. This incredible processing speed allows you to respond to visual threats before you’re even aware you’ve seen them.
Your brain accomplishes this through a complex network of neural pathways dedicated to visual processing.
The Complex Human Body
These fascinating facts merely scratch the surface of the incredible complexities within the human body. From microscopic cellular processes to large-scale organ systems, our bodies perform countless remarkable functions every second of every day.
Understanding these lesser-known aspects of human physiology helps us appreciate the extraordinary machine we call home.
More from Go2Tutors!

- Famous Battles: How Much Do You Really Know About U.S. History?
- Top 5 Most Important Skills, According To Harvard Business School
- How Well Do You Know 90s Pop Culture? Take the Quiz
- Master the Art of Public Speaking with These Expert Tips
- Think You Know Capitals? Put Your Knowledge to the Test
Like Go2Tutors’s content? Follow us on MSN.



