20 Jaw-Dropping Facts About the Deep Ocean
The deep ocean remains Earth’s last great frontier, with over 80% of our planet’s waters still unexplored. Scientists continue to discover astounding new species, geological features, and phenomena in these mysterious depths.
From crushing pressures to bioluminescent creatures, the deep ocean holds secrets that challenge our understanding of life itself. Here’s 20 jaw-dropping facts about our ocean that boggle the mind.
The Midnight Zone
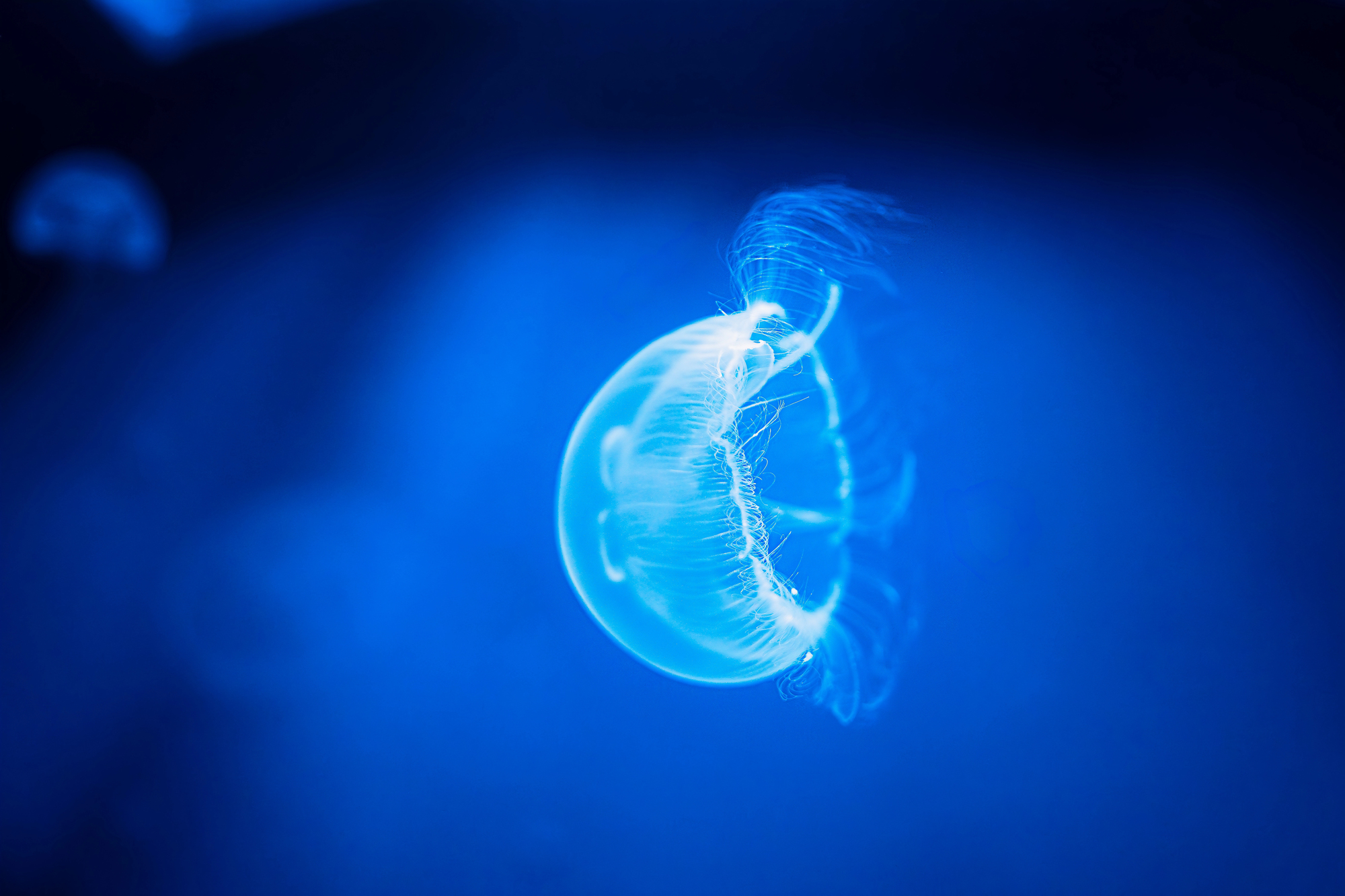

At depths below 1,000 meters, sunlight completely disappears, creating a realm of perpetual darkness known as the midnight zone. Marine life here has evolved extreme adaptations to survive, including ultra-sensitive eyes, bioluminescence, and the ability to detect minute vibrations in the water.
Hydrothermal Vents
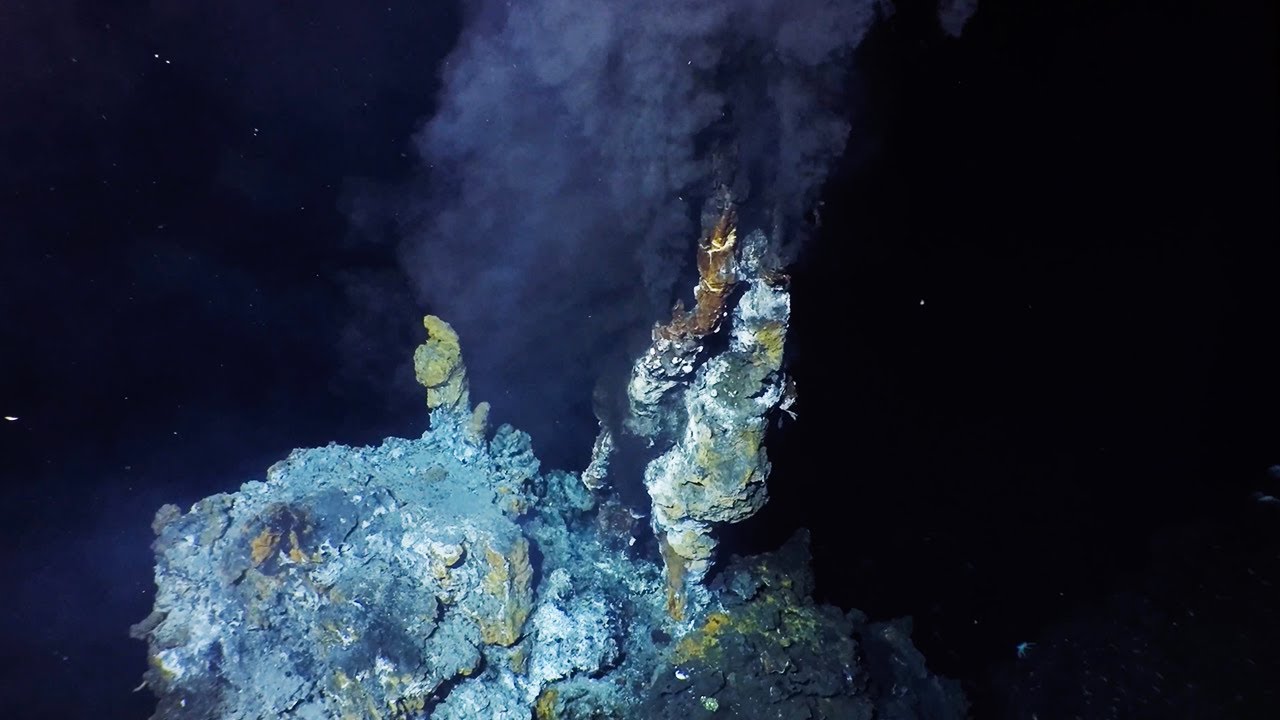

These underwater geysers spew water heated to temperatures exceeding 400°C, yet thriving communities of organisms live around them. The extreme pressure at these depths prevents the water from boiling, creating unique chemical conditions that support chemosynthetic bacteria and complex food webs.
Like Go2Tutors’s content? Follow us on MSN.
Giant Squid Territory

The elusive giant squid can grow to lengths of 43 feet and possesses eyes the size of dinner plates. These massive creatures weren’t successfully filmed in their natural habitat until 2012, demonstrating how much remains unknown about deep-sea life.
Pressure Extremes

At the ocean’s deepest point, the Challenger Deep, pressure exceeds 15,750 psi – equivalent to 50 jumbo jets stacked on top of a person. Only specially designed submarines and a handful of organisms can withstand these crushing depths.
The Deep Scattering Layer
A mysterious layer of the ocean appears solid on sonar due to millions of marine organisms moving up and down daily. This massive migration, spanning hundreds of meters vertically, represents the largest animal movement on Earth by biomass.
Like Go2Tutors’s content? Follow us on MSN.
Immortal Jellyfish
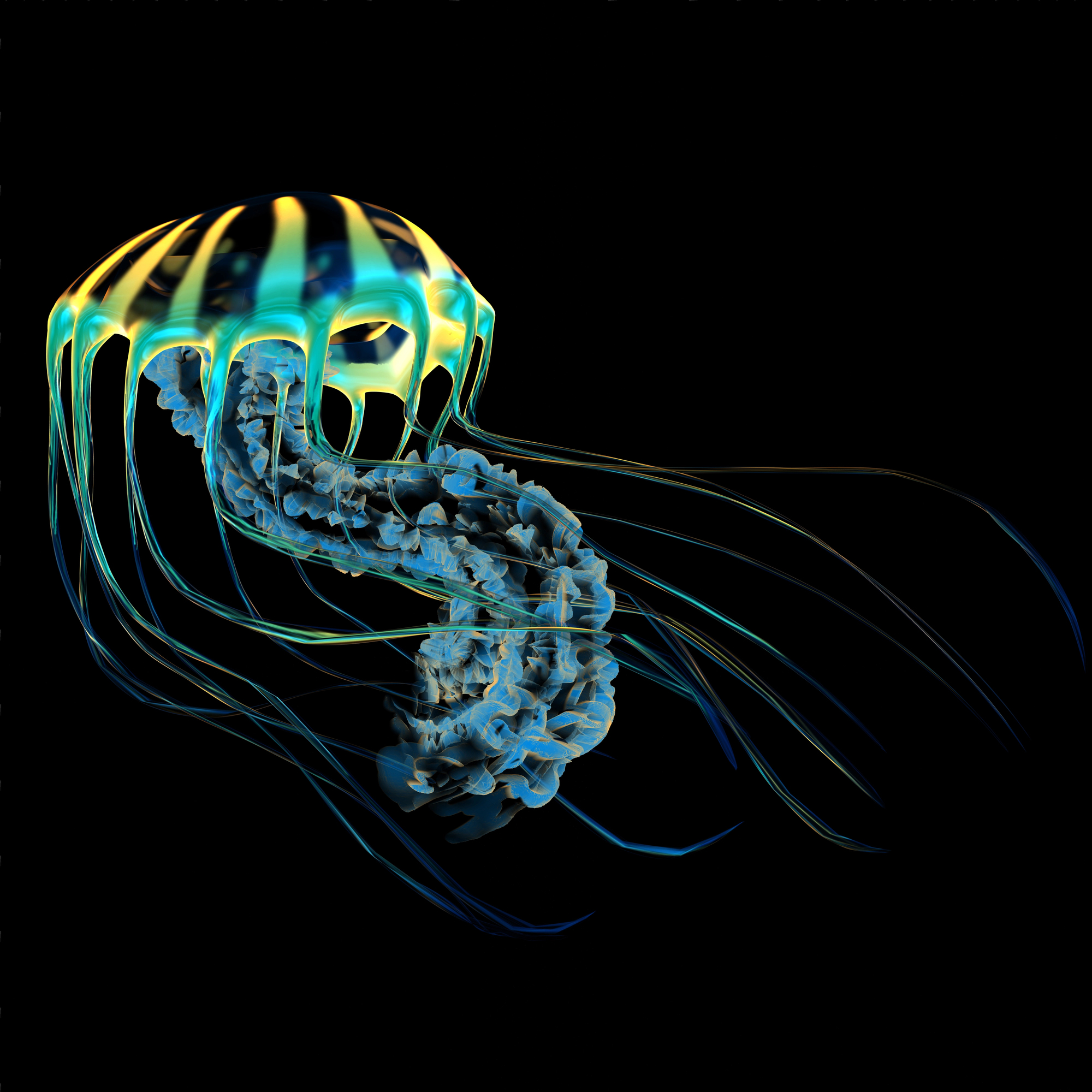
The Turritopsis dohrnii, found in deep waters, can theoretically live forever by reverting to an earlier stage of development when stressed or injured. This unique ability makes it the only known potentially immortal creature on Earth.
Ancient Waters

Scientists have discovered pockets of seawater in the deep ocean that haven’t mixed with surface waters for over 1,000 years. These ancient waters provide valuable data about historical ocean conditions and climate patterns.
Living Fossils
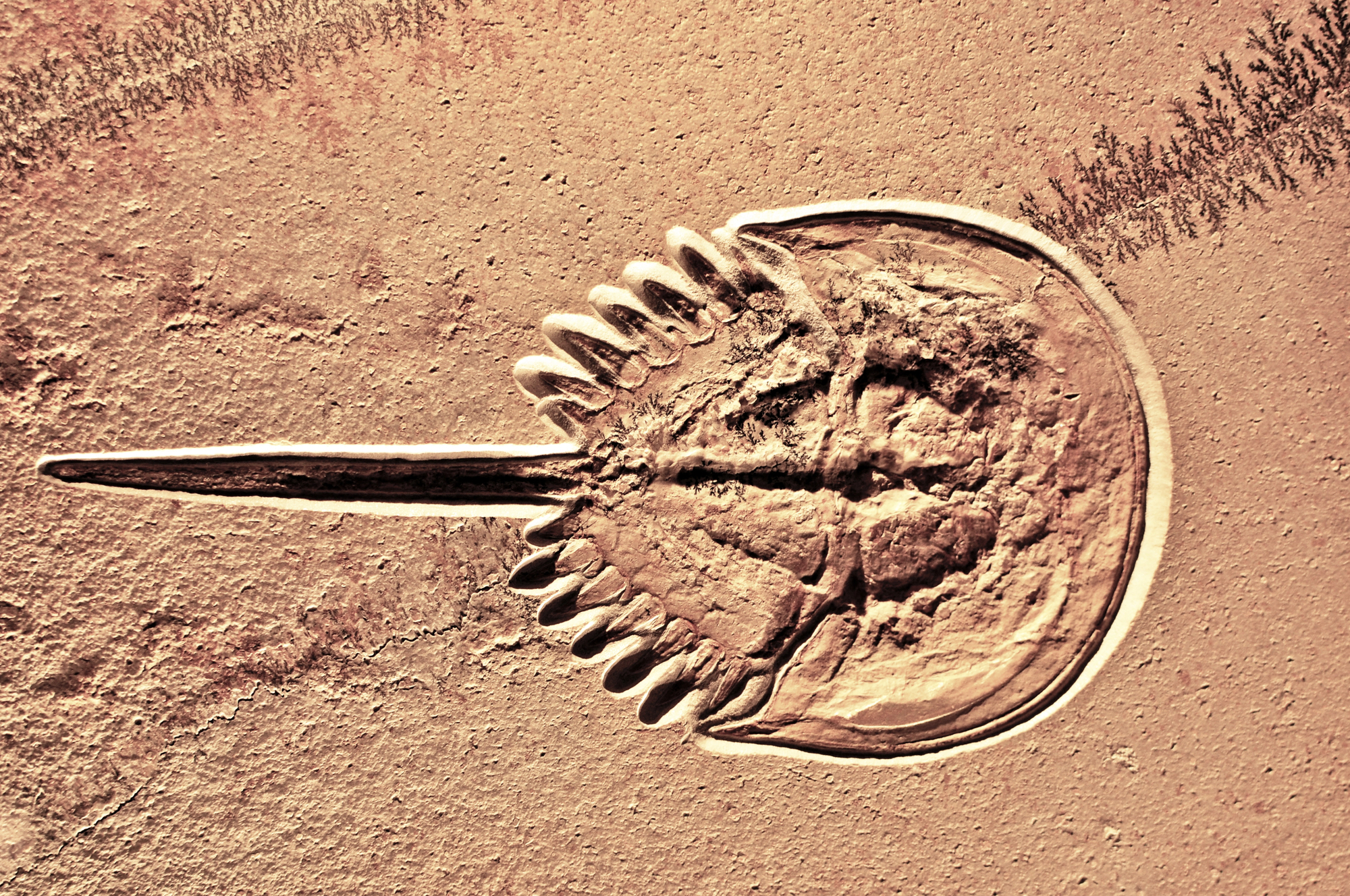
The coelacanth, thought extinct for 66 million years, was discovered living in deep waters off South Africa in 1938. These ancient fish demonstrate how deep-ocean environments can preserve species that disappeared elsewhere.
Like Go2Tutors’s content? Follow us on MSN.
Underwater Lakes

The deep ocean contains lakes of extra-salty water with their own shorelines, waves, and distinct ecosystems. These brine pools are so dense that submarines can actually ‘float’ on their surface.
Bone-Eating Worms

Osedax worms, discovered in 2002, specifically evolved to digest whale bones on the seafloor. These bizarre creatures drill into bones using acid-secreting roots and absorb nutrients through tree-like structures.
The Loudest Animal
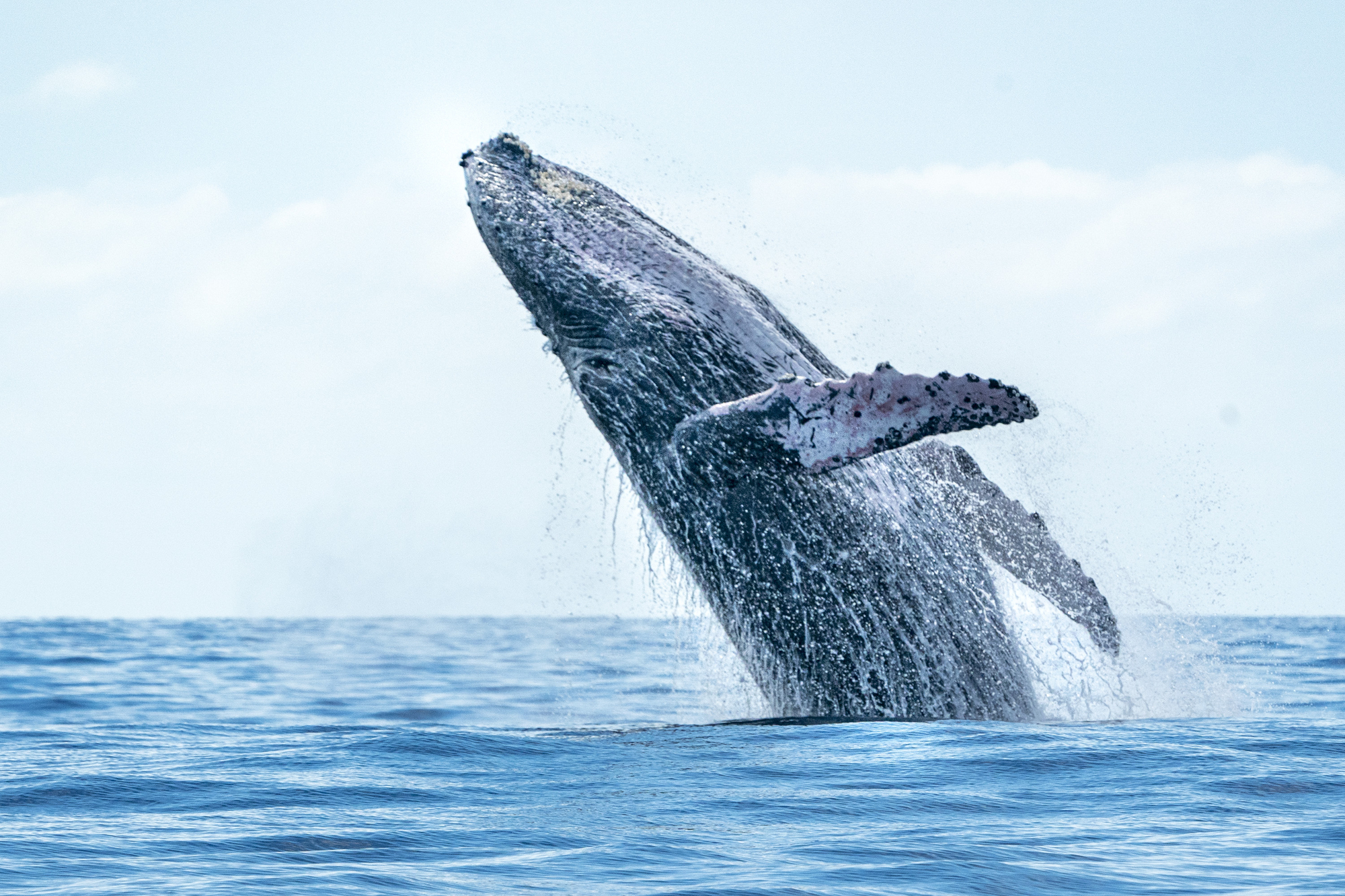

The sperm whale’s echolocation clicks can reach 230 decibels underwater, making it the loudest animal on Earth. These sounds can be detected across entire ocean basins, allowing whales to communicate over vast distances.
Like Go2Tutors’s content? Follow us on MSN.
Volcanic Activity
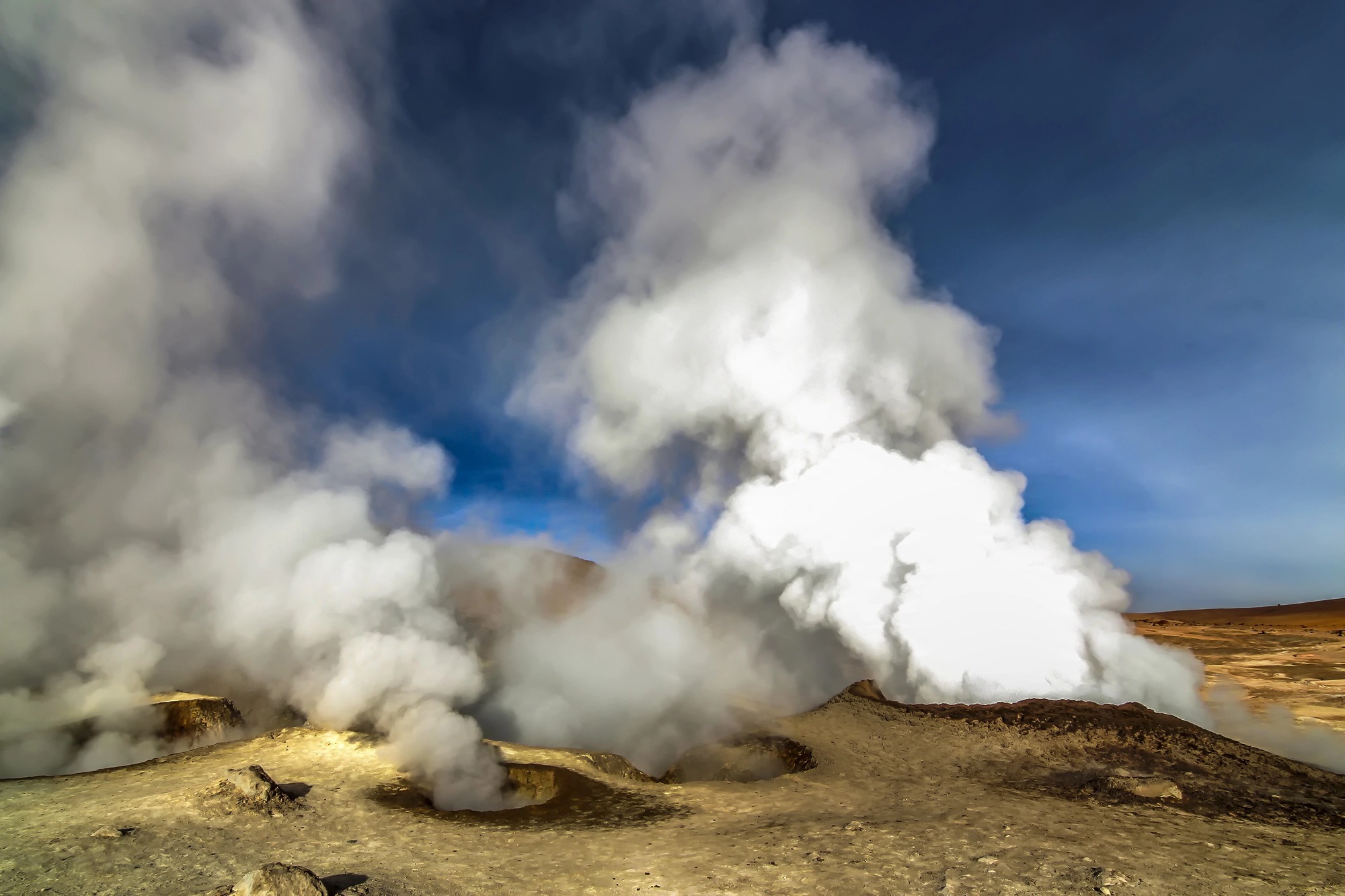

Approximately 75% of Earth’s volcanic activity occurs underwater, with most eruptions going unnoticed. These submarine volcanoes create new seafloor and support unique ecosystems through mineral-rich emissions.
Plastic Pollution Depths

Scientists have discovered plastic debris in the deepest ocean trenches, including microplastics in creatures living 36,000 feet below the surface. This reveals how human activities impact even the most remote environments.
Temperature Extremes

While most deep ocean water hovers around 4°C, temperatures near hydrothermal vents can exceed 400°C just inches away from near-freezing waters. This creates unique thermoclines that support specialized life forms.
Like Go2Tutors’s content? Follow us on MSN.
Carbon Storage
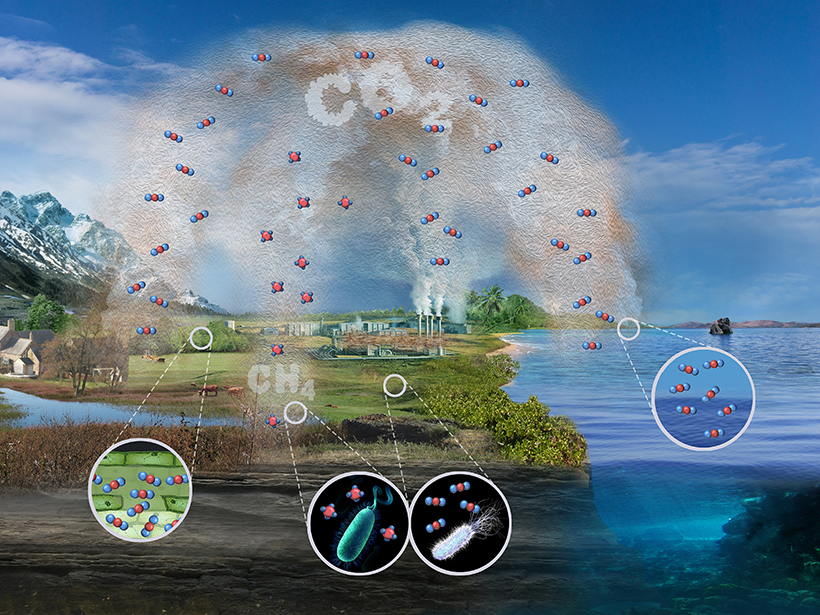

The deep ocean serves as Earth’s largest carbon sink, storing about 50 times more carbon dioxide than the atmosphere. This massive carbon reservoir plays a crucial role in regulating global climate.
Bioluminescent Majority

About 90% of marine organisms living in the mesopelagic zone can produce their own light through bioluminescence. This ability serves various purposes, from communication to hunting and defense.
Unexplored Trenches

Ocean trenches cover an area larger than Australia, yet less than 20% have been explored. Each survey of these depths reveals new species and geological features previously unknown to science.
Like Go2Tutors’s content? Follow us on MSN.
Pressure-Loving Microbes
Scientists have discovered microorganisms that not only survive but require extreme pressures to live. These piezophiles cannot function properly when brought to surface pressures, demonstrating unique evolutionary adaptations.
Living Snow

Marine snow, composed of dead organisms and organic matter, constantly falls through the deep ocean like an underwater snowstorm. This continuous shower of nutrients sustains deep-sea ecosystems far from the sunlit surface.
Eternal Darkness

The abyssopelagic zone, ranging from 4,000 to 6,000 meters deep, experiences constant darkness and near-freezing temperatures year-round. Life forms here have evolved extraordinary sensory capabilities and often lack pigmentation due to the complete absence of light.
Like Go2Tutors’s content? Follow us on MSN.
Beyond the Horizon

Despite technological advances and centuries of exploration, our oceans continue to surprise us with new discoveries. From unknown species to mysterious phenomena, the deep ocean remains a testament to Earth’s endless capacity to amaze and challenge our understanding of life itself.
More from Go2Tutors!

- Famous Battles: How Much Do You Really Know About U.S. History?
- Top 5 Most Important Skills, According To Harvard Business School
- How Well Do You Know 90s Pop Culture? Take the Quiz
- Master the Art of Public Speaking with These Expert Tips
- Think You Know Capitals? Put Your Knowledge to the Test
Like Go2Tutors’s content? Follow us on MSN.



