19 Medical Myths That Were Widely Believed (and Completely Wrong)
People have believed countless medical misconceptions throughout history, from ancient healing practices to surprisingly recent misunderstandings about the human body. Medical knowledge evolves constantly as science advances and new discoveries emerge.
Here’s a list of 19 medical myths that were once considered medical facts but have since been thoroughly debunked by scientific research.
Sugar Causes Hyperactivity

The idea that sugar triggers hyperactive behavior in children gained momentum in the 1970s. Multiple controlled studies showed absolutely no link between sugar consumption and hyperactivity in children.
A major research project in 1994 specifically tested different sugar levels in children’s diets, finding no behavioral changes. Parents often noticed increased energy because sugar was typically consumed at exciting events like parties and holidays, creating a false correlation.
Humans Only Use 10% of Their Brain

This persistent myth gained widespread acceptance in the early 1900s. Modern neuroimaging techniques clearly show activity throughout the entire brain, with different regions constantly working together.
Even during sleep, the brain remains highly active, managing essential bodily functions and processing memories. The brain actually consumes about 20% of the body’s total energy, making it impossible for 90% to sit idle.
Like Go2Tutors’s content? Follow us on MSN.
Cold Weather Causes Colds

Victorian-era doctors firmly believed exposure to cold temperatures directly caused illness. The real culprit behind seasonal colds is viruses, which spread more easily in winter when people spend more time indoors in close contact.
The cold environment actually helps preserve the virus particles longer outside the body, increasing transmission rates. Body temperature changes don’t create or activate the cold virus.
Reading in Dim Light Damages Vision

This belief gained traction during the Industrial Revolution when poor lighting was common in workplaces. While reading in low light can cause temporary eye strain and discomfort, numerous studies have found no permanent damage to vision.
The eyes naturally adjust to different light levels, much like a camera lens adapting to changing conditions. Regular breaks help prevent eye fatigue regardless of lighting conditions.
Cracking Knuckles Causes Arthritis

Parents and grandparents worldwide warned children about this supposed danger. A doctor named Donald Unger famously cracked the knuckles of only his left hand for 60 years to test this theory.
His research showed no difference in arthritis between his hands. The popping sound comes from gas bubbles in the joint fluid, not from bones or cartilage grinding together.
Like Go2Tutors’s content? Follow us on MSN.
Feed a Cold, Starve a Fever

This 16th-century advice stemmed from the belief that colds resulted from a drop in body temperature. The body actually needs consistent nutrition to fight any illness effectively.
Both colds and fevers increase the body’s energy requirements as it works to fight infection. Proper hydration and regular meals support the immune system’s ability to combat both conditions.
Swimming After Eating Causes Cramps

This widespread summer safety myth claimed waiting an hour after eating prevented dangerous cramping. While blood flow does shift slightly toward digestion after meals, the effect isn’t significant enough to impair swimming ability.
The American Red Cross found no documented cases of drowning caused by swimming on a full stomach. Simple common sense about individual comfort levels provides better guidance.
Ulcers Come From Stress

Medical professionals believed stress and spicy foods were the primary causes of stomach ulcers until the 1980s. Australian researchers Barry Marshall and Robin Warren discovered the true cause: H. pylori bacteria.
Their findings revolutionized ulcer treatment, shifting from stress management to antibiotics. Marshall famously proved the bacterial connection by drinking a culture of H. pylori, developing ulcers, and then curing himself with antibiotics.
Like Go2Tutors’s content? Follow us on MSN.
Blood is Blue Inside the Body
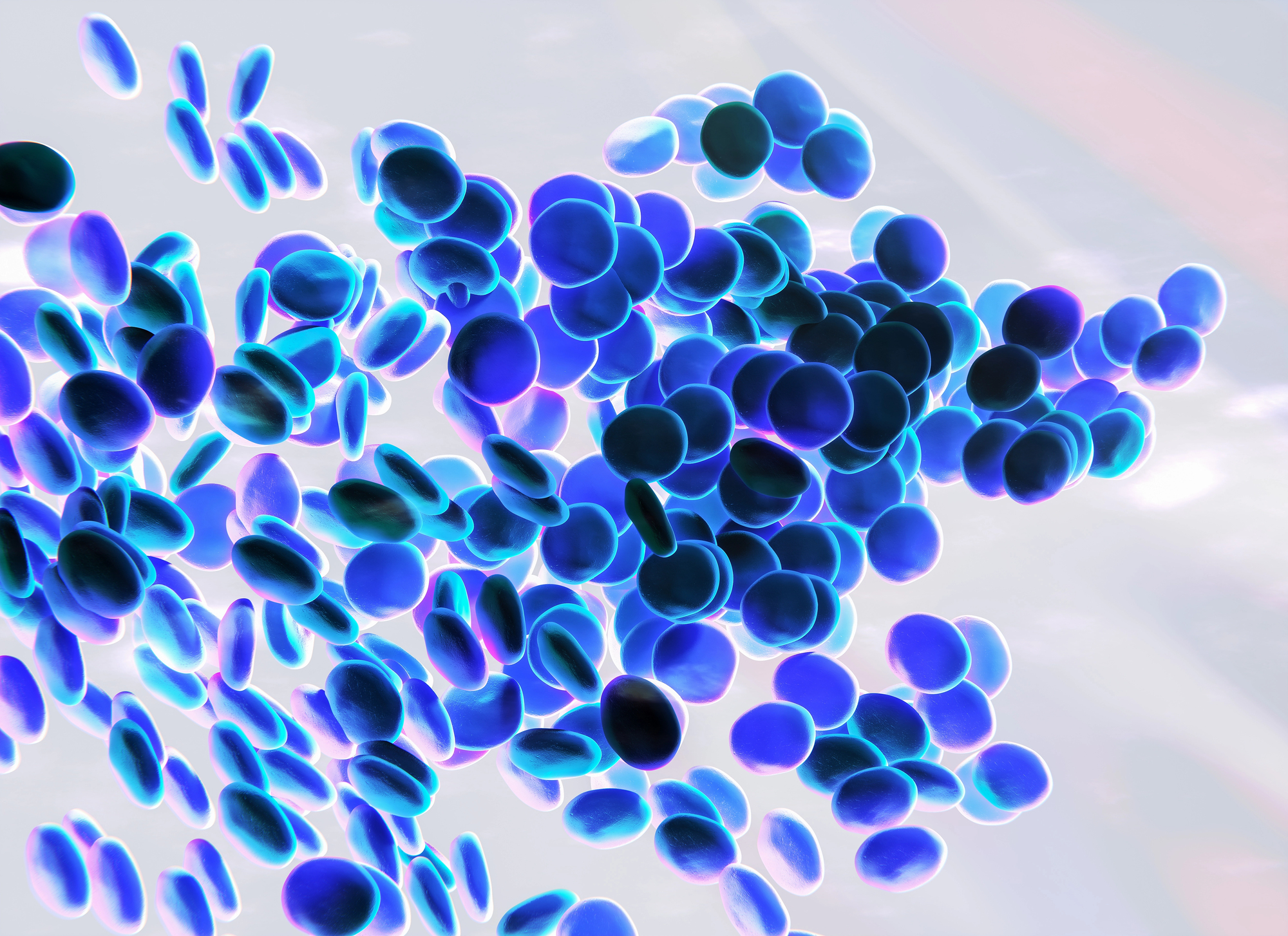
This misconception arose from the appearance of veins through skin. Deoxygenated blood appears darker red, not blue, while oxygenated blood maintains a bright red color.
The bluish appearance of veins results from how light interacts with skin and blood vessels. Ancient anatomists who performed dissections clearly observed red blood throughout the body, but the myth persisted in popular culture.
Shaved Hair Grows Back Thicker

This belief gained popularity during World War II when young men first started shaving regularly. The cut hair shaft might feel coarser initially, but careful measurements show no change in thickness or growth rate.
The blunt tip of freshly cut hair creates an illusion of thickness compared to the natural tapered end. Numerous studies since the 1920s have consistently disproven this myth.
Vitamin C Prevents Colds

Nobel laureate Linus Pauling popularized this idea in the 1970s. While vitamin C supports immune function, extensive research shows it doesn’t prevent colds in the general population.
Regular supplementation might slightly reduce cold duration, but the effect remains minimal. The body can only absorb and use a limited amount of vitamin C, making megadoses unnecessary and potentially wasteful.
Like Go2Tutors’s content? Follow us on MSN.
Coffee Stunts Growth

Parents often used this warning to keep children away from caffeine. Extensive research has found no connection between coffee consumption and reduced growth.
Height is primarily determined by genetics and overall nutrition. The myth likely originated from coffee’s ability to temporarily affect calcium absorption, though this effect proves negligible in a balanced diet.
Wet Hair Causes Pneumonia

Generations of mothers insisted children thoroughly dry their hair before going outside. Pneumonia develops from bacterial or viral infections, not from temperature changes or wet hair.
The body maintains its core temperature effectively regardless of wet hair. This myth probably emerged when people associated going outside with wet hair in winter with catching seasonal illnesses.
Chocolate Causes Acne

Dermatologists in the 1960s and ’70s commonly advised against chocolate consumption to prevent breakouts. Modern research shows no direct link between chocolate and acne formation.
Hormonal changes, genetics, and certain medications play much more significant roles in acne development. The myth likely persisted because teenagers, who experience hormonal acne, often consume more chocolate.
Like Go2Tutors’s content? Follow us on MSN.
MSG Causes Headaches

The ‘Chinese Restaurant Syndrome’ scare of the 1960s villainized monosodium glutamate. Controlled studies repeatedly failed to find a consistent connection between MSG and headaches in the general population.
The FDA classifies MSG as ‘generally recognized as safe,’ and it occurs naturally in many foods like tomatoes and cheese. The nocebo effect often explains reported symptoms.
Alcohol Warms the Body

This dangerous myth dates back centuries when alcohol was used as a treatment for hypothermia. Alcohol actually causes blood vessels to dilate, making people feel warmer while losing body heat more rapidly.
This misconception proved particularly dangerous for winter travelers who felt deceptively warm while experiencing dangerous drops in core body temperature.
Carrots Dramatically Improve Vision

British intelligence spread this myth during World War II to hide their radar technology. While carrots contain vitamin A, essential for eye health, eating extra carrots won’t enhance vision beyond normal levels.
The body only uses the amount of vitamin A it needs, storing or discarding the excess. The military’s clever disinformation campaign created a lasting public health myth.
Like Go2Tutors’s content? Follow us on MSN.
Swallowed Gum Takes Years to Digest

Parents often terrified children with warnings about gum remaining in their digestive system for seven years. The digestive system handles gum like any other non-nutritive substance, passing it within a few days.
While frequent gum swallowing isn’t recommended, occasional accidents cause no lasting harm. The body efficiently moves the gum through the digestive tract without absorption.
Arthritis Can Predict Weather
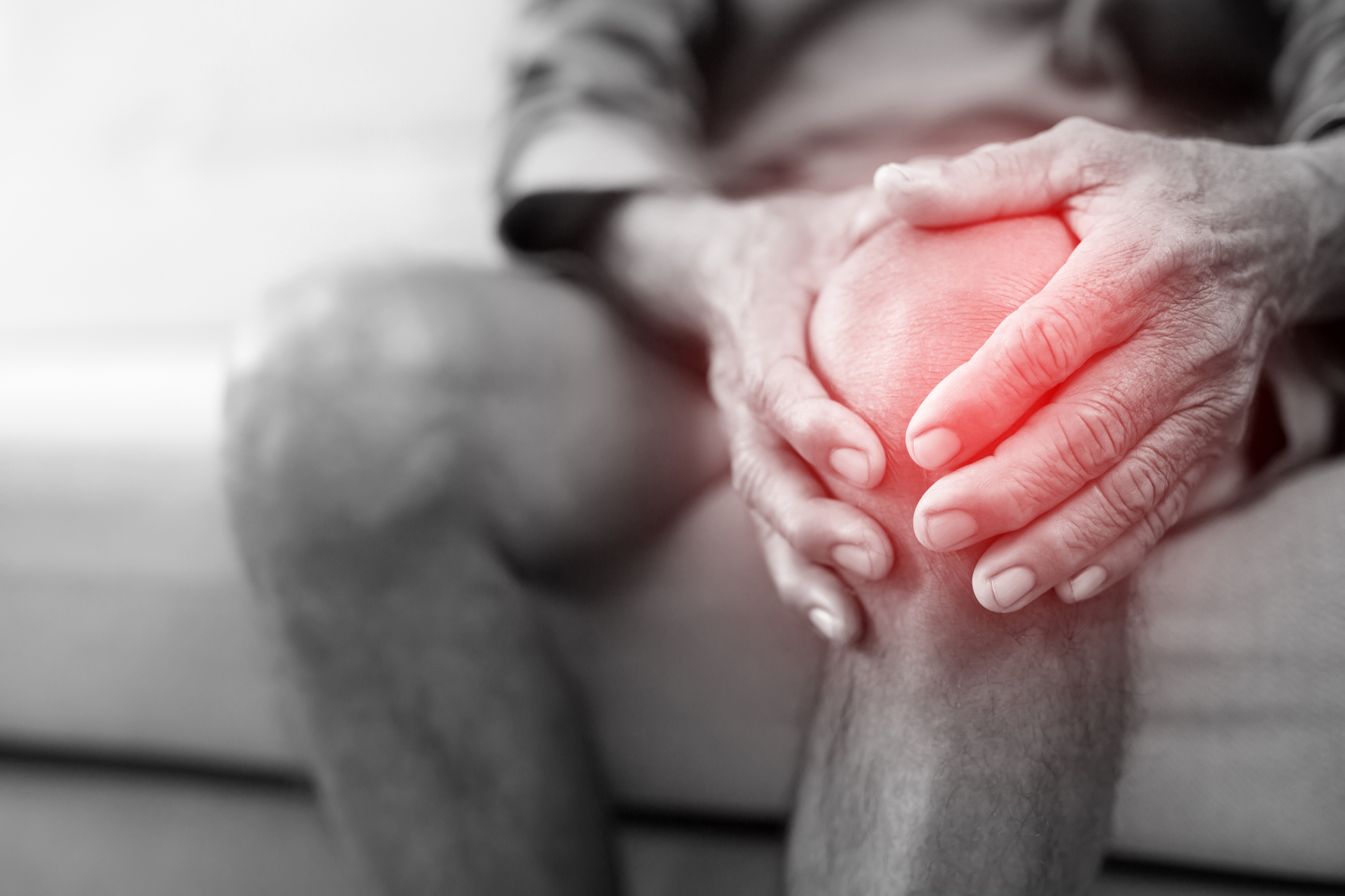

Many people firmly believed their joint pain accurately forecasted weather changes. While some patients report increased discomfort during weather changes, scientific studies show no consistent correlation between joint pain and weather patterns.
Changes in activity levels and mood during different weather conditions might explain the perceived connection.
Medicine’s Evolution Continues

Today’s medical facts might become tomorrow’s myths as research advances our understanding of the human body. Modern science continues to challenge long-held beliefs, reminding us to maintain healthy skepticism and stay informed about medical developments.
The journey from myth to fact shapes our growing knowledge of human health.
More from Go2Tutors!

- 20 Historical Artifacts That Scientists Can’t Explain
- 15 Unforgettable Candy Bars From The 60s and 70’s That Disappeared Too Soon
- 20 Countries That No Longer Exist and What Happened to Them
- 20 Forgotten Fast Food Items From the 80’s That Need to Come Back
- Famous Battles: How Much Do You Really Know About U.S. History?
Like Go2Tutors’s content? Follow us on MSN.



